If search engines can’t understand your website, they can’t rank it properly.
That’s where website architecture and crawlability come in.
These two concepts form the foundation of technical SEO. When done right, they make your site easier for search engines to explore and easier for users to navigate—leading to better rankings, more traffic, and higher conversions.
This guide breaks everything down in simple language, with real-world examples you can apply immediately.
What Is Website Architecture?
Website architecture is the way your website’s pages are organized, grouped, and connected.
Think of it like a building:
- The homepage is the main entrance
- Categories or sections are the floors
- Individual pages are the rooms
A good architecture answers three questions clearly:
- What is this website about?
- What are the main topics or services?
- How do individual pages relate to each other?
Simple example (blog or business site)
Home
├── Blog
│ ├── SEO
│ ├── Content Marketing
│ └── Analytics
├── Services
│ ├── SEO Services
│ └── Web Design
└── Contact
When pages are logically grouped like this, both users and search engines know where everything belongs.
How Website Architecture Impacts SEO & Crawlability
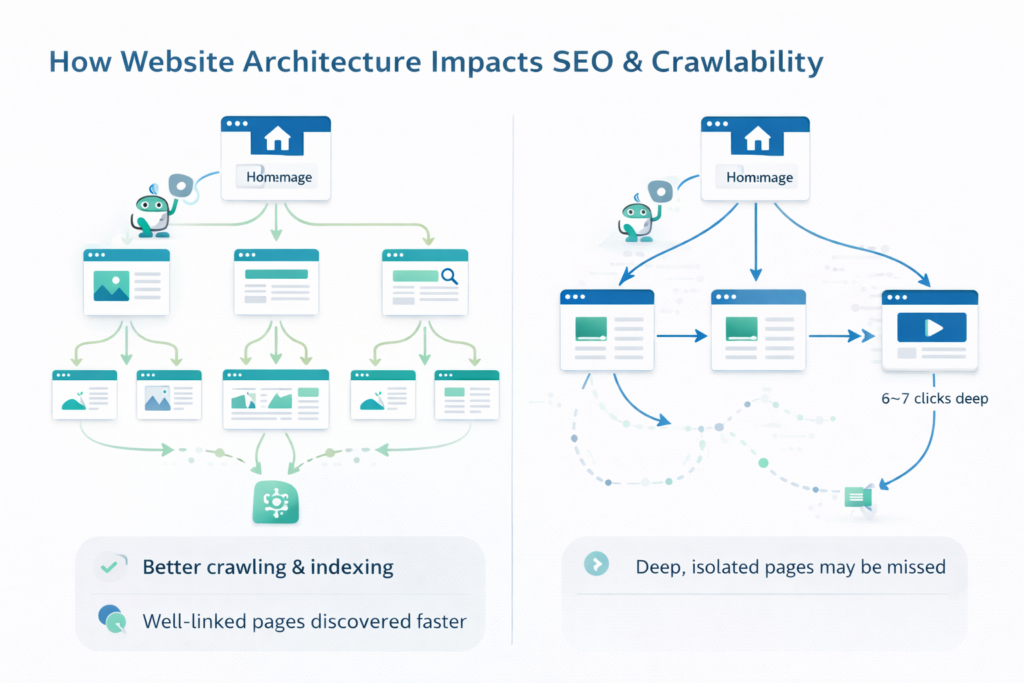
Search engines use automated bots to crawl your website by following links. Your architecture directly affects how efficiently that happens.
A strong structure helps SEO in three major ways:
1. Better Crawling & Indexing
Pages that are well linked and not buried deep in the site are discovered faster and crawled more often.
If an important page is:
- 6–7 clicks away from the homepage
- Not linked from any other page
…it may be crawled less frequently or even missed.
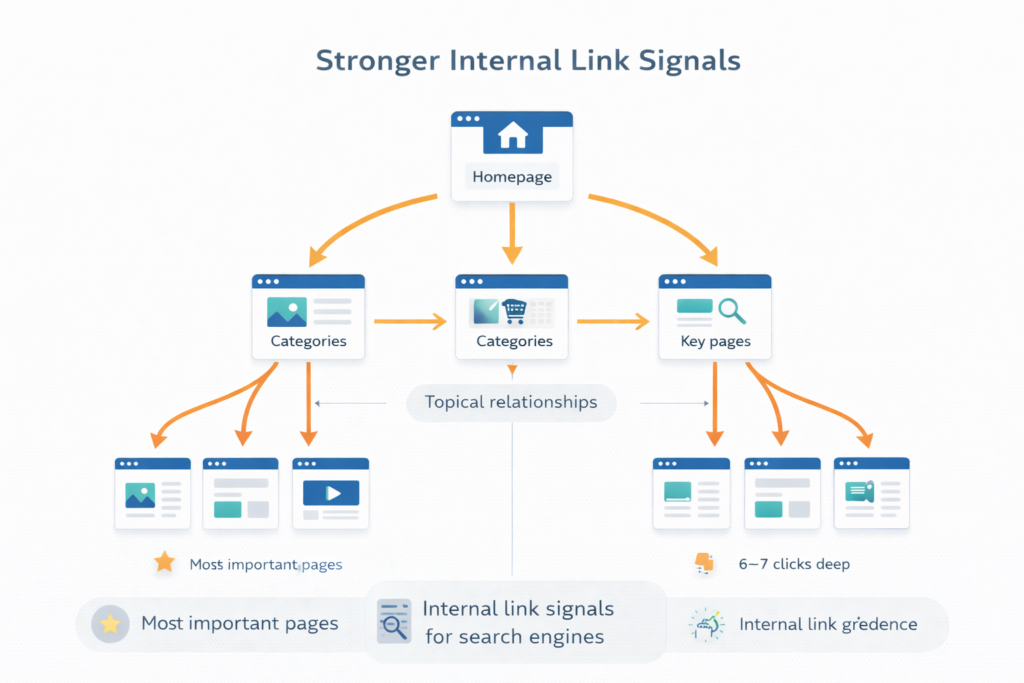
2. Stronger Internal Link Signals
Search engines use internal links to understand:
- Which pages are most important
- How topics are related
A clear architecture naturally pushes authority from:
Homepage → Categories → Key pages
This helps your most valuable pages rank better.
3. Better User Experience (UX)
Good structure isn’t just for bots.
When visitors can quickly find:
- Products
- Services
- Information
…they stay longer, explore more pages, and convert at higher rates.
SEO and UX improve together.
Flat vs Deep Structure: What’s the Difference?
Flat Website Structure
A flat structure means most pages can be reached in 3–4 clicks or less from the homepage.
Example (flat):
Home → Blog → SEO Article
Home → Services → Local SEO
Benefits:
- Faster crawling
- Better internal link flow
- Easier navigation for users
Flat structures are ideal for:
- Blogs
- Small to mid-size ecommerce stores
- Local business websites
Deep Website Structure
A deep structure pushes pages far down into multiple layers.
Example (deep):
Home → Blog → Marketing → SEO → Technical → Tags → Article
Problems:
- Pages receive less link authority
- Crawling becomes inefficient
- Users get lost
Deep structures often happen accidentally as sites grow without planning.
How to Design a Simple, Scalable Site Hierarchy
A good hierarchy starts broad and becomes more specific.
Recommended approach
- Homepage – overall brand or business
- Main sections – blog, services, shop, locations
- Categories – topics or product groups
- Individual pages – posts, products, service details
Example: Ecommerce site
Home
├── Men
│ ├── Shoes
│ └── Jackets
├── Women
│ ├── Dresses
│ └── Accessories
└── Sale
This structure scales easily. You can add new products without breaking the logic.
Categories and Hub Pages (Why They Matter)
Hub pages act as central points for related content.
Examples of hubs:
- Blog category pages
- Service overview pages
- Product category pages
Why hubs are powerful
- They organize content clearly
- They concentrate internal links
- They help search engines understand topical authority
Blog example
/blog/seo/= SEO hub- Links to all SEO-related articles
- Each article links back to the hub
This creates a strong topical cluster.
URL Structure That Supports Architecture
Your URLs should reflect your site structure.
Good URL examples
/blog/seo/technical-seo-basics//services/local-seo//shop/mens/shoes/running-shoes/
Simple URL rules
- Use readable words, not IDs
- Match folder structure to hierarchy
- Avoid unnecessary parameters
- Use hyphens, not underscores
When URLs mirror architecture, search engines understand relationships faster.
Internal Links & Avoiding Orphan Pages
Internal links are the glue that holds your architecture together.
They help:
- Bots discover pages
- Users navigate naturally
- Authority flow to important content
Best practices
- Link from category pages to all important child pages
- Link between related blog posts
- Link from content pages back to hub pages
- Link to key commercial pages where relevant
Avoid orphan pages
An orphan page has no internal links pointing to it.
These pages:
- Are hard to discover
- Often don’t rank well
- Waste content effort
Every important page should have at least one internal link.
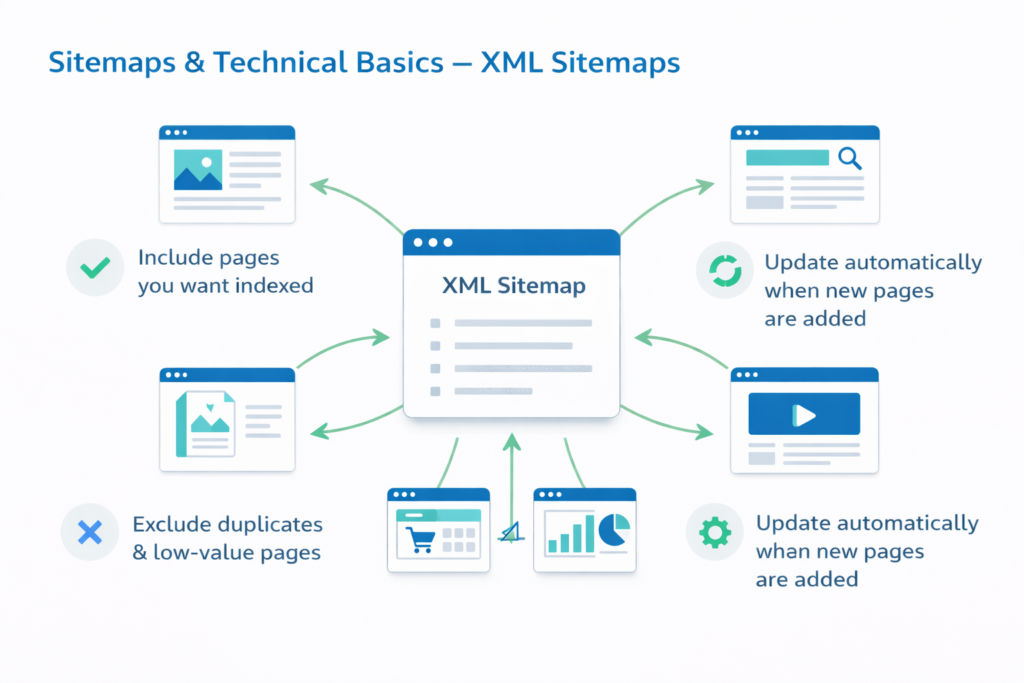
Sitemaps & Technical Basics
XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is a list of important URLs that helps search engines discover content.
Good practice:
- Include pages you want indexed
- Exclude duplicates or low-value pages
- Update automatically when new pages are added
Robots.txt
This file controls crawler access.
Be careful:
One wrong rule can block entire sections of your site.
Broken Links & Errors
Too many:
- 404 pages
- Redirect chains
- Server errors
…can waste crawl budget and harm user experience.
Regular site audits help prevent this.
Sitelinks & Other Benefits of Good Architecture
A clean structure increases the chances of earning:
- Google sitelinks (extra links under your main result)
- Better breadcrumb display
- Improved rich results eligibility
These features improve:
- Click-through rates
- Brand visibility
- User trust
Good architecture supports SEO beyond just rankings.
Practical Website Architecture Checklist
Use this checklist to review your site:
- Key pages reachable in 3–4 clicks or less
- Clear hierarchy from homepage to content
- Categories or hubs for major topics
- Clean, descriptive URLs
- Strong internal linking between related pages
- No orphan pages
- XML sitemap submitted and updated
- Navigation simple and HTML-based
- Broken links regularly fixed
